How Would You Describe British Tax Policies in the Colonies
The Stamp Act was completely repealed. The idea behind this economic policy was that the colonies.

Taxation Without Representation Lesson Overview Article Khan Academy
No American would be allowed west of the Allegheny Mountains.

. Some of the taxes that were imposed on the colonies of North America were the Wool Act Hat Act Iron Act Molasses Act Navigation Acts Sugar Act Revenue Act Sugar act Stamp Act. Introduced by the British Parliament in 1765 the Stamp Act was an internal tax which few colonists could escape all of the colonists were drastically affected by this tax. In modern times this has meant more and higher taxes rarely fewer and lower taxes.
The Sugar Act was passed by Parliament in April of 1764. It culminated with the Boston Tea Party. I t is said that taxes are the price we pay for a civilized society.
The Colonial Roots of American Taxation 1607-1700. The American Revolution was precipitated in part by a series of laws passed between 1763 and 1775 that regulating trade and taxes. Laws passed between 1763 and 1775 regulated trade in the colonies and imposed new taxes to refill British coffers.
For the first time the British had levied an explicit tax on the colonist for the purpose of raising revenue previous taxes were seen as trade taxes and tolerated by colonial residents. Prior to 1750 British essentially followed a policy of benign neglect and political autonomy in the American colonies. The Townshend Act with the exception of.
In the Western European democracies the tax take. An example of an external tax is the Sugar Act passed in 1764 which raised costs only for a select group of people. The act placed a tax on sugar and molasses imported into the colonies.
However that did not mean the colonists were satisfied with the British govern-ment. Lawrence Gibson Historian 1930. Public opposition to the tax was minute.
When the Seven Years War began it made Britain fall into debt and the solution was to tax even more the colonists - many taxes and trade restrictions such as the Stamp Act. How did opposition to British tax policies affect the American colonies. 1764 Parliament passed the Currency Act which banned the use of paper money as legal tender in all colonies.
The tax bite in the United States is one-third of the gross domestic product gdp. Parliamentary taxation of colonies international trade and the American Revolution 17631775. This legislation caused tensions between colonists and imperial officials who made it clear that the British Parliament would not address American.
Although most of the Townshend duties had been. The act was also intended to stop trade between the colonies and the Dutch French and Spanish. Not only did they lack representation but they were also treated as second class citizens who they took advantage of in order to only benefit themselves.
British mercantilism flourished during the middle of the 17th century at a time when England was flexing its muscle in the New World. It led to high tensions with Britain. The relations between England and the British North American colonies could always be considered precarious.
Great Britain reasoning for the taxes was that it helped pay for the seven year war and that the colonies should also to help pay since the soldiers of Great Britain is still there to. This affected Boston and New England greatly because the colonists there used sugar and molasses to make rum. Since the war benefited the many American colonists from England the British government reasoned colonists should help pay for it.
British merchants had asked for relief from the depreciated currency brought about by deficit financing in Virginia. A Dispute Over Tea During the early 1770s the protests in the colonies against British policies quieted down. The act represented an effort to wrest control of monetary policy from colonial assemblies.
We would describe it as unfair because the colonies didnt even have representation in the parliament yet they were expected to pay taxes. Evolution of British Policy in the Colonies. When the British throne was passed to George III things got even more strained between the Colonies and the British government.
The British tax policies as unfair to the colonies. Parliament refused to respond to colonial concerns sparking the Revolutionary War. At the end of the war the British Parliament sought to replenish its depleted coffers by taxing the North American.
The Sugar Act. Both were taxes that were assessed against the British American colonies. British Taxation Policies After the conclusion of the Seven Years War in 1763 the British Empire was in financial distress.
Opposition to the tax was widespread as it represented an infringement on their rights. How did British tax policies move the colonists closer to rebellion. The British were selfish since instead of.
The British were justified in taxing the Americans and tightening the navigation acts after 1763 because it had been largely British blood and money that was expended in defending the North American colonies in the Great War for Empire 1754-1763. Though the British had won the war they had spent vast amounts of blood and treasure in the process. It led to boycotts of British goods.
For example Britain forced the colonists to pay taxes in order to repair the economic damage done by the French and Indian War. Davidson p97 The colonies were for the most part content with benign neglect policy.

Townshend Acts Definition Facts Purpose History
Topic 2 2 Taxed By England South Carolina History

Britain S Law And Order Strategy And Its Consequences Us History I Os Collection
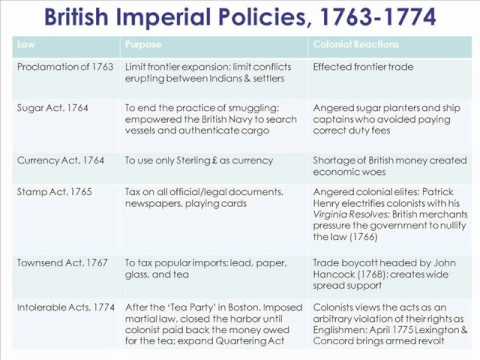
Supporting Question 2 How Did British Policies Inflame Tensions In The American Colonies Lessons Blendspace
Comments
Post a Comment